Computational Social Science
When defining Computational Social Science (CSS), a central theme consistently emerges: the use of advanced computational methods to analyze large-scale datasets with the aim of understanding and interpreting human behavior. What distinguishes CSS is not merely its focus on social phenomena, but its reliance on computational techniques and extensive data to achieve insights.
CSS rests on two primary pillars: Network Analysis and Social Simulation.
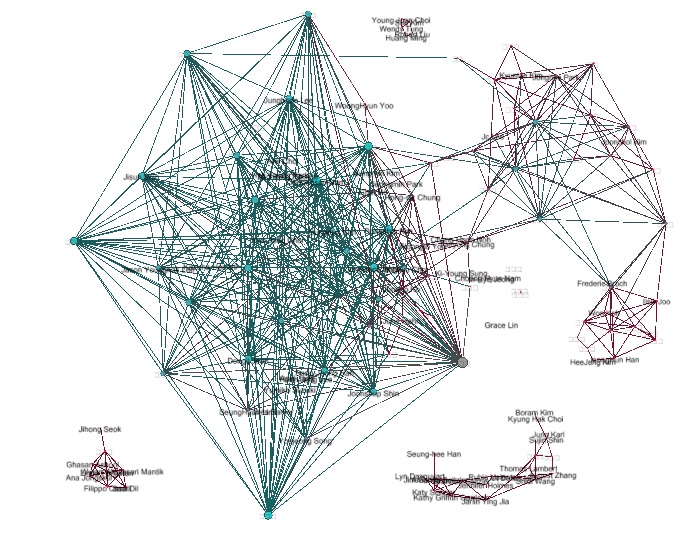
Network Analysis has flourished with the availability of rich relational data and advancements in computational tools, enabling more robust and data-driven exploration of complex social structures and interactions.
Social Simulation, on the other hand, takes a model-driven approach, using computational models to simulate and study emergent patterns and behaviors within social systems.
Computational Social Science 1 (Network) Computational Social Science 2 (Simulation)